Oxygen performs an essential role in preserving health of the body. Oxygen along with glucose are the principal nutrients every cell needs to produce energy for all its life processes. These functions involve molecule transportation, chemical compound synthesis and mechanical operations like contraction of muscles. Numbering in the thousands, these functions are occurring at all times, which enable the body to pump blood, fight infections, digest food, and process neural information.
Ozone is produced naturally through flashes of lightning, as well as photochemical reactions of UV light on atmospheric oxygen. Nature’s purpose in this production of ozone is air purification, and destruction of organic decay that disease, germs and bacteria thrive upon. Ozone, like oxygen, functions as a healthful gas. The difference is ozone provides more antiseptic, germicidal and oxidizing power.
Respiration processes cause waste products to be subjected to interactions with oxygen in the air. The result is these waste products are burned off in a similar fashion to being placed in a stove, which produces body heat. In the human body, this heat is constantly being produced by way of chemical reactions between carbon and oxygen.
Once the blood acquires adequate oxygen to combine with the carbon, CO2 (carbon dioxide) is formed, which the body then considers to be suitable for elimination. The oxidation process is completed, body temperature is maintained at 98.6° F, organs function properly, and the whole system can resist toxic influences of behavioral choices, microbes and the environment.
However, when the blood receives an insufficient amount of oxygen, carbon monoxide (CO) is formed. Carbon Monoxide is not readily eliminated and presents a troublesome and poisonous influence. Carbon monoxide acts as a deoxidizer. It is an irritant to the body’s organs, which lowers body temperature below normal, creating a diseased state that is incapable of resisting bacteria, viruses and other environmental toxins. Subnormal temperature is prevalent among people who are exhausted or run down, and can be detected in nine out of every ten of these patients by a thermometer.
Possessing sufficient levels of oxygen for the blood results in better blood, improved circulation, increased assimilation, balanced equilibrium of body temperature, greater vasomotor activity, more effective digestion, more efficient elimination of waste, lower chance of toxemia/autointoxication, and reduced opportunity for infection and disease.
Analytical disease investigations have demonstrated among the most important factors a person can correct is weakness produced by a diminished blood supply. Under oxidation produces poor health mainly because a lack of oxygen almost always results in formation of carbon monoxide. The reputation of carbon monoxide is as de-oxidizer, destroyer of hemoglobin and irritant toxin that devitalizes the blood and paves the way for acute problems, which often become chronic.
Ozone Therapy has been used successfully in Europe for many years. Basically, oxygen therapy is classified depending on the kind of chemical reaction involved: Oxygenation will involve adding oxygen to blood or tissues, while oxidation entails the transferring oxygen electrons.
Oxygenation therapy saturates the body with oxygen. Oxygen is absolutely essential for the cells, tissues, organs and biological functions of the body. Oxygen is necessary for good health, but too little can boost the development of harmful bacteria along with viruses, and too much could harm tissue that is healthy. Oxygen therapy absolutely requires the instruction and expertise of a trained practitioners.
An assortment of disorders such as stress, illness, poor diet, shallow breathing and insufficient lung performance can all result in oxygen depletion throughout the body. This allows disease-causing microbes that flourish in low-oxygen conditions to multiply, negatively impacting your wellness. Studies have even suggested that low oxygen concentrations in the blood can certainly be a factor adding to premature aging. The work of Otto Warburg, a two-time Nobel laureate, reveals that a shortage of oxygen on a cellular level could possibly be a major contributor to cancer. His experiments using tissue cultures demonstrated that oxygen therapy can certainly destroy cancer cells.
Oxygen therapy seeks to rebuild optimal cell function. Oxygen therapy can be clinically administered in several ways: intravenously, intra-arterially, orally, vaginally, rectally, or through skin injection. Oxidation therapy is quite different than oxygen therapy. Oxidation represents a chemical reaction whereby electrons are shifted between different molecules. Oxygen molecules are usually needed for these reactions, but not necessarily. The electron donating molecule is recognized as oxidized, while the receiving molecule is called oxidants.
Oxidation occurs naturally and is a necessary operation of the body, however the body’s oxidative ability may be destabilized by exposure to stress and toxins. Using oxidation treatments can kick start the human body’s natural oxidative systems, while eradicating disease-producing microbes, bacteria, and viruses. Oxidative therapies also function to deactivate harmful substances, while healthy tissues remain uneffected. For example, when topical applications of hydrogen peroxide are made to wounds, the healthy cells blossom while pathogens and bacteria perish. Hydrogen peroxide as well as ozone are commonly used for oxidation therapy.
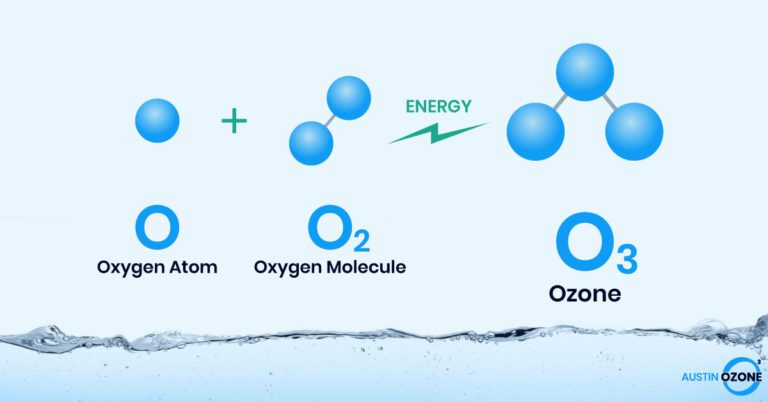
Ozone therapy is distinctive because it is equally oxidative and oxygenating. The secret is contained in ozone molecules. Where by oxygen is made up of 2 oxygen molecules or O2, ozone consists of 3 oxygen molecules or O3, making it substantially less stable. The added oxygen molecule of ozone means that it is much more reactive than normal oxygen and will readily enter into oxidative chemical reactions. During the oxidation process, ozone’s extra oxygen molecule is released to bond to another molecule. This leaves a ordinary O2 molecule, which results in increased oxygen in blood, tissues and organs.
Ozone is actually anti-bacterial, anti-viral, and anti-fungal in function. Therefore, it is effective in treating a variety of health concerns including burns, slow-healing wounds, skin ulcers, chronic infections, and viruses. Ozone treatments are administered using many different techniques: topically, subcutaneously and intravenously are all popular. When water is enhanced with ozone, it can also be presented orally, rectally and vaginally. Due to the fact that ozone is harmful when inhaled, only a trained specialist should administered the treatment. Research indicates that consuming vitamin C supplements together with ozone therapy can be necessary to minimize uncontrolled oxidation that can be unsafe.
Oxygen and ozone therapy both have robust, health supporting results for many individuals. The broad range of health troubles that may be overcome by these remedies may indicate they are due for a resurgence in recognition.