Urinary tract infection (UTI) is a type of bacterial infection that affects 60% of women and 12% of men8 at some point in their lives. Contrary to popular belief, Urinary Tract Infection does not only affect the urinary tract but can also include the urethra, ureters, bladder, and kidneys.
How the Urinary System Works?
After carrying the essential nutrients for energy conversion, the human blood carries the remaining waste products to the body’s excretory system.
The urinary system’s main function is to filter the blood and remove the wastes from the body in the form of urine. The organs in the urinary system include the urethra, bladder, ureters, renal pelvis, bladder, and kidneys.
Urine is mainly composed of the urea – a liquid chemical produced when the proteins you ate (e.g., meat, poultry, some types of vegetable, etc.) are broken down for their nutrients. Urea is carried through the bloodstream and removed along with the other wastes and water. The kidneys filter the urea from the blood, after which it is carried through the ureters to the bladder where urine is temporarily stored.
The urinary system’s main function is to filter the blood and remove the wastes from the body in the form of urine. The organs in the urinary system include the urethra, bladder, ureters, renal pelvis, bladder, and kidneys.
The nerves in the bladder usually alert the person if and when it is time to urinate (or empty the bladder). When this happens, the urine is allowed to pass through the urethra and expelled from the body. Normal urination occurs when all the signals appear in the correct order. A healthy urine is usually a transparent yellow in color.
Urinary Tract Infection occurs when bacteria enter the urinary system, irritating the bladder and urethra linings. This irritation can cause pain or a burning sensation and will make you feel like urinating more frequently than usual. At times, the urge to urinate is so strong that you may lose control of your bladder and leak urine.
Urinary Tract Infection should not be ignored as the infection may spread to your kidneys and can become a life-threatening issue.
What Causes Urinary Tract Infection?
Although a lot of bacteria – the skin’s natural microfauna – thrive in the genital area, the main reason for the development of Urinary Tract Infection is when bacteria from the large intestine (usually, E. Coli) travels from the anus into the urethra. It is also possible to get the bacteria through sexual intercourse. From there, the bacteria will travel upward to the bladder and may continue to the kidneys.
Since women have shorter urethras than men, they are more prone to developing UTI. In addition, anatomical abnormalities (like an enlarged bladder or an enlarged prostate gland) and health issues (like diabetes) can increase the chances of getting UTI.
Types of Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary Tract Infections can be classified into two types: simple and complicated. A simple Urinary Tract Infection is usually treated by taking antibiotic medications and plenty of liquids. Those who are at their menopausal stage can also treat a simple UTI with topical hormone replacement.
Complicated Urinary Tract Infections are more difficult to treat. These are Urinary Tract Infections that occur as a result of structural abnormalities in the urinary system, a compromised immune system, or which involve antibiotic resistant bacteria. They often require intravenous antibiotic therapy as well as oral antibiotics. The symptoms of Urinary Tract Infection should improve after a few days of taking the treatment, although you need to complete the treatment process to ensure that the UTI is fully cured; otherwise, the infection can recur with worse and more virulent symptoms.
Depending on which part is infected, UTI can be found in any of these three sections: the urethra (urethritis), the bladder (cystitis), and the kidneys (pyelonephritis).
Urinary Tract Infection Treatment: The Problem With Antibiotics
Antibiotics are drugs that are used to treat bacterial infections. However, it is completely possible for bacteria to develop resistance in response to these medicines. This makes infections more difficult to treat, leading to prolonged hospital stays, higher medical costs, and increased mortality rates.
The number of drug-resistant bacteria has been steadily increasing5 these past few years. Even when new drugs are developed, bacteria can still develop a resistance against them. This has necessitated health care providers to find non-pharmacologic methods3 like ozone therapy to use for diseases like the UTI.
Ozone gas has well-known antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, anti-inflammatory, and analgesic effects, as well as the ability to modulate the immune system and reactivate microcirculation.
Schedule an Ozone Therapy Session Today!
History of Ozone Therapy
The existence of ozone gas was discovered in 1840 when scientist Christian Schonbein noticed a distinct odor when he directed an electric current through water. Ozone’s ‘clean’ smell propelled medical professionals to study it further for its health benefits.
By 1856, ozone gas was being used as a disinfectant in operating rooms and as a way to sterilize surgical tools. Ozone gas was further studied as a possible wound disinfectant during World War I.
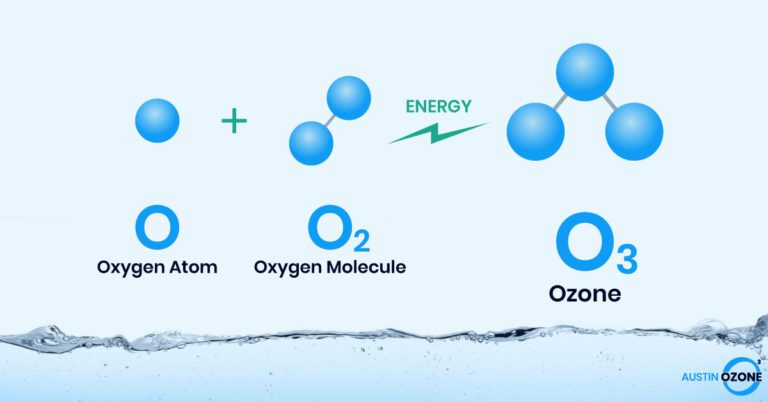
Today, medical grade ozone is made by passing pure oxygen gas through a crystal tube where an electric spark is directed. The electrical energy breaks the oxygen molecule into two singular oxygen atoms for a few seconds. However, because these split molecules are highly unstable, they will pair up again to produce a mixture of oxygen (made up of two oxygen atoms) and ozone (composed of three oxygen atoms).
Ozone therapy is the introduction of medical ozone gas into the body through various methods. Potential routes include intravenous, intramuscular, nasal, ear, vaginal, and rectal.
Ozone therapy is the introduction of medical ozone gas into the body through various methods. Potential routes include intravenous, intramuscular, nasal, ear, vaginal, and rectal. According to experts7, medical ozone stimulates the oxidative and anti-oxidative pathways that help with the regeneration and healing of injured tissues.
In addition, ozone therapy has no reported collateral effects, as it does not cause any toxic or allergic reactions, making it the best form of alternative procedure for Urinary Tract Infection treatment.
Ozone Therapy as Treatment for Urinary Tract Infection
Since bacteria is the main cause for Urinary Tract Infection, antibiotics are usually used as the main form of treatment. However, most bacteria are known for developing resistance to antibiotics, thus, it is the interest of healthcare providers to employ treatment that inhibits bacteria from sticking to the organs, thereby reducing the risk of infection1.
Medical ozone has been consistently used for its potent antibacterial properties, ability to regulate the immune system, and ability to reduce the oxidative stress6 that can contribute to chronic infection.
As a bactericidal agent, it can take several different forms, which include ozonated water, ozonated oil, ozonated saline solution, or the most common form, oxygen/ozone gas mixture. The high oxidation potential of ozone gas targets the cellular membranes of the bacteria that eventually leads to their deterioration.
Antibiotic resistance increases among patients, ozone therapy offers a concrete alternative for addressing infections such as the Urinary Tract Infection.
In a case study5 of a 67-year old female patient with chronic cystitis caused by a multi-drug resistant E. coli, ozone therapy via major autohemotherapy (MAH) showed positive results in removing the infection from the bladder lining.
Another study2, which was conducted in New Zealand, demonstrated the successful reduction of inflammation of the basal membrane in a rabbit’s infected bladder through intravesical insufflations.
Considering that antibiotic resistance increases among patients, ozone therapy offers a concrete alternative for addressing infections such as the Urinary Tract Infection.
Risks and Safety Concerns in Using Ozone Therapy for UTI Treatment
Ozone therapy is a non-invasive and generally painless procedure. Although there are no major collateral effects reported, it is still possible to experience some minor adverse effects. For example, there are some who experience faster heart rates, fever, and a sudden drop in blood pressure.
There’s also the risk of experiencing the Herxheimer reaction7 – a phenomenon where the body releases endotoxin-like chemicals caused by the removal of harmful microorganisms during treatment.
Summary
Urinary Tract Infection is a type of bacterial infection that should not be ignored as it can have dire consequences when left untreated. The infection can potentially spread from the urinary tract to the bladder and kidneys. When this happens, UTI can lead to serious health complications that can be life-threatening.
While antibiotics are still considered the most common treatment for Urinary Tract Infection, patients undergoing this form of medication have higher chances of developing antibiotic resistance, prompting more expensive types of treatment. In a world where diseases evolve faster than the cure, alternative therapies are considered glimpses of hope for better recovery.
Ozone destroys the bacteria’s cellular membrane and activates a complex series of chemical reactions to effectively eliminate the bacteria from the body.
Although many research and clinical studies are needed to determine the true efficacy of ozone therapy in Urinary Tract Infection treatment, the few studies that exist all show positive results in reducing inflammation and eliminating the source of infection in the bladder.
MAH seems to be the most effective ozone therapy method used, followed by intravesical insufflations. Unlike antibiotics, bacteria will not be able to build a resistance against ozone. Ozone destroys the bacteria’s cellular membrane and activates a complex series of chemical reactions to effectively eliminate the bacteria from the body.
Schedule an Appointment Today
References
- American Chemical Society. (2012, June 20). Non-antibiotic approach for treating urinary tract infections. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2012/06/120620113338.htm
- Bayrak, O., Ertuhan, S., Ilker, S., Erbagci, A., Ustun, A., & Karakok, M. (2014). Chemical cystitis developed in experimental animals model: Topical effect of intravesical ozone application to bladder. Urology Annals, 6(2),122-126. doi: 10.4103/0974-7796.130553
- Bonforte, G., Bellasi, A., Riva, H., Ferradini, M., Arrighi, E., Groppi, G., Minoretti, C., & Franzini, M. (2013). Ozone therapy: A potential adjunct approach to lower urinary tract infection? A case series report. Giornale Italianodi Nefrologia, 30(4), gin/30.4.16
- Integrative Wellness NY. (n.d.). OZONE THERAPY FOR INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (NATURAL TREATMENT) IN BROOKLYN NY. Retrieved from I
- Logan, K. (2018). Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBL-EC) producing escherichia coli urinary tract infection treated with ozone therapy. Revista Española de Ozonoterapia. 8(1), 145-152
- Rowen, R. (2018). Ozone therapy as a primary and sole treatment for acute bacterial infection: case report. Medical Gas Research, 8(3), 121-124. doi: 10.4103/2045-9912.241078
- Stuber, J. (2017, July 30). Book review: ‘Ozone: The miracle therapy’. Retrieved from https://samaritanministries.org/blog/ozone-therapy-miracle-therapy
- Urology Care Foundation. (2019, April). What is a urinary tract infection (UTI) in adults? Retrieved from https://www.urologyhealth.org/urology-a-z/u/urinary-tract-infections-in-adults